How to find the real digital potentials in the Circular Economy

Digital Revolution in everybody’s mind
It can be seen as given, that we are right in the middle of the so-called digital revolution. Being a buzzword, the term generates a lot of momentum. That is of course positive, but sometimes it even scares business decision makers. Breaking it down, it is nothing to be afraid of. It is as simple as it can be. Digital refers to electrified 0s and 1s. Those 0s an 1s are translated to bits and bytes, if arranged next to each other, which are then translated into information. That information really provides the value. It supports decision making or even enables automated decisions (artificial intelligence, AI). It is now called a revolution because information is generated faster and faster - at incredible speed. 90 percent of the data, which is available now, has been generated over the last two years.
Digitalization and its potential
It is not surprising that companies are investing heavily in digitalization to keep pace. The prove is easy - looking at annual reports of global acting waste management and recycling companies, nearly every CEO mentions the identified and untapped potential of digitalization. Lots of projects are triggered and investments are being made. But do these investments always aim at the right potentials?
Apparently, the awareness for necessary actions exists. But - structured and straight forward ways to identify the right potentials are often lacking. Companies in the circular economy which are of course experts in their current business processes, often face a hard time to creatively embrace digital elements. A common reason for that is the lack of an easy-to-understand model what digital transformation means. OECD recently published an interesting approach which could also help to map the components attached to the term digitalization “the confluence of key technologies enabling the industry digital transformation”. Although being generic, the elements are absolutely valid.
The confluence of key technologies enabling the industrial digital transformation
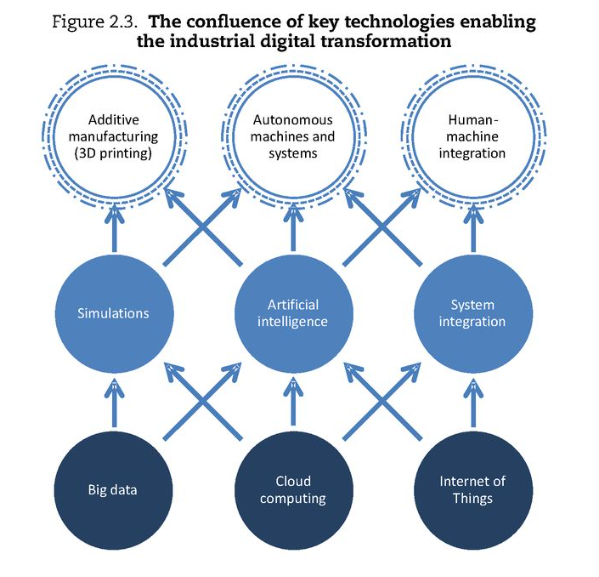
Looking at it in more detail, big data, cloud computing and internet of things together are the key elements to start with. The term big data refers to data characterized by its volume (huge), velocity (fast) and variety (unstructured or structured). It was made possible by increased storage capacities and processing technologies. Cloud computing allows computing resources to be scaled up and down easily. Physical objects connected to information flows in addition represent the internet of things (IOT). One of the keys to integrate processes, services and products. Together, IOT, big data and cloud computing are the major reasons for the sudden breakthrough of the above simulations, artificial intelligence, and system integration elements (second row of the graph). System integration from an organizational perspective means to come across organizational silos (departments) and collaborate based on technological platforms. The elements given in the top row are built upon simulations, AI and system integration. The top row speaks for itself – 3D printing, autonomous machines or human machine integration, also referred to user experience.
Intelligent assistants are expanding the potential of conventional ERP systems. How can you boost your strategic decisions? Decide for an intelligent and customized ERP system!
How can that easy model be applied to the waste and recycling industry?
At Cosmo Consult, we have already seen a combination of the main elements of the model in several projects so far. The following list provides an overview of these applications, followed by the main elements of the introduced model:
- Preemptive maintenance for cost intensive assets/machinery (main elements: IOT, big data, AI)
- Route optimization for fuel efficiency and maximized usage (main elements: Big data, cloud, AI)
- Integration of on-board units (main elements: IOT, cloud, system integration)
- Remote access to container data e.g. for filling grades (main elements: IOT, cloud, autonomous machines and systems)
- Global supply chain integration (main elements: Cloud, system integration)
- Performance contracting (main elements: AI, big data)
- Improved traceability e.g. implementation of camera on waste trucks (main elements: IOT, big data)
- Portals for bidding or contracting (main elements: Cloud, system integration)
- Mobile apps for guiding drivers to jobs (main elements: Human machine integration, cloud)
- Predict services tasks for containers in the field (main elements: IOT, AI, autonomous machines and systems)
Like other industries the processes within waste industry are individualized. Therefore, there are many reasons why you should definitely think about an industry solution instead of a standard ERP. Curious?
Individual assessment is essential
Of course, the model is only one approach that helps to find out what digitalization can unleash. The individual value must be assessed in the context of a clients’ business model. The model shall help to trigger own future perspectives or can even provide guidance to derive future business scenarios. Or even better: Let’s find out your real digital potentials together.

